Dr Alan Cheung
Senior Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon in Singapore
MBBS (London), MRCS (England), FRCS (Trauma and Orthopaedics, England), Diploma in Sport and Exercise Medicine (UK), Fellow of the European Board of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS)
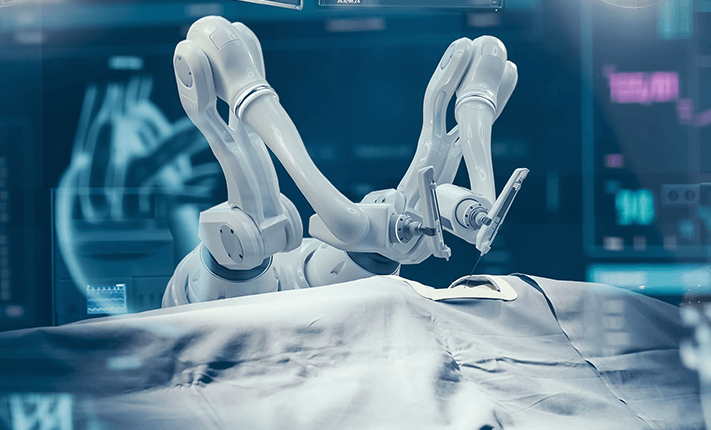
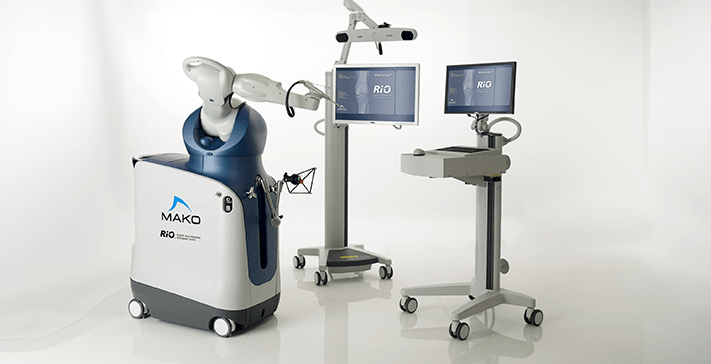
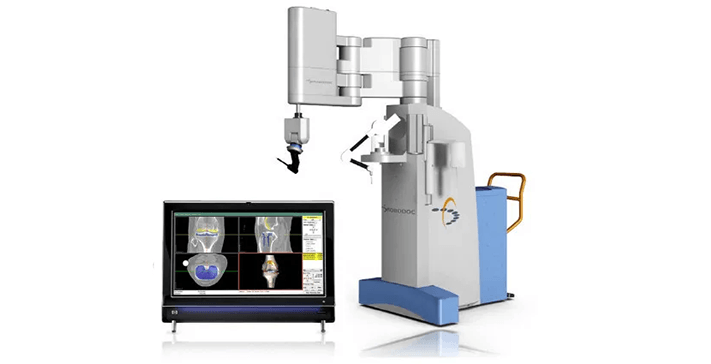
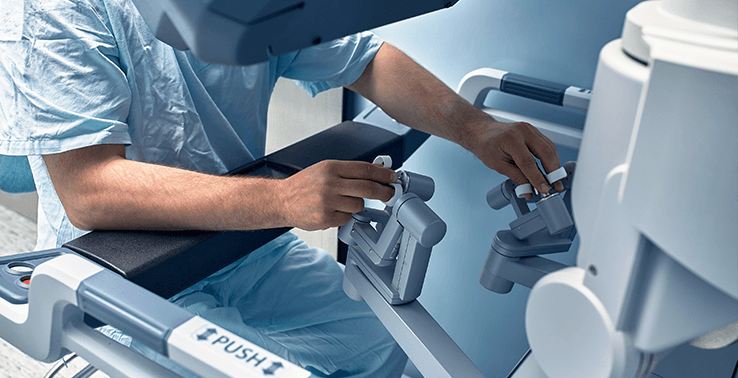
What is Robotic Surgery?
Robotic surgery is an advanced medical technique that integrates robotic systems with
surgical procedures to enhance precision, accuracy, and patient outcomes. These systems
provide surgeons with greater control, allowing for minimally invasive procedures that
reduce trauma to surrounding tissues.
In orthopaedic surgery, robotic systems assist in joint replacements, spinal surgeries,
and other musculoskeletal procedures by providing detailed preoperative planning and
real-time intraoperative guidance.
Although excellent results can be achieved using conventional joint replacement techniques, Dr Alan Cheung believes that robotic surgery can give increased accuracy, better preoperative planning, and reliable, reproducible results particularly in technically challenging and revision cases.