What is Arthroscopy?
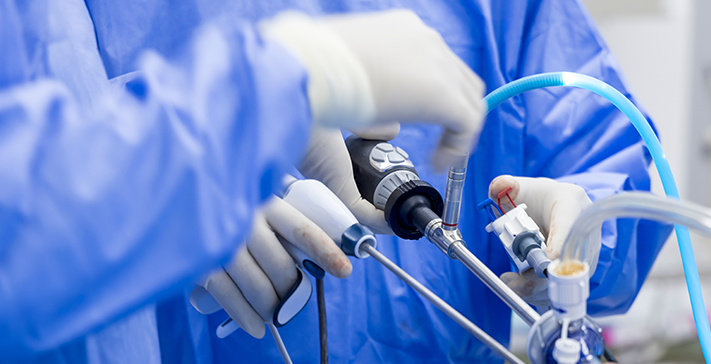
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used by orthopaedic surgeons to diagnose and treat joint problems. It involves inserting a small camera, called an arthroscope, through a tiny incision to view the inside of a joint in real time. This allows for precise evaluation and treatment of conditions affecting joints such as the knee, shoulder, hip, and wrist without the need for large incisions.
Benefits of Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, including:
Minimally Invasive: Smaller incisions result in less tissue damage and scarring
Faster Recovery Time: Patients typically heal quicker than with open surgery
Reduced Pain and Swelling: Less trauma to surrounding tissues leads to lower post-operative discomfort
Lower Risk of Complications: Reduced risk of infections and blood clots compared to open surgery
Outpatient Procedure: Most patients can return home the same day, reducing hospital stays
Improved Diagnostic Accuracy: Direct visualization of joint structures helps in precise diagnosis and targeted treatment