Senior Consultant Orthopaedic Knee Surgeon | Director of the International Orthopaedic Clinic (IOC)
MBBS (London)
MRCS (Royal College of Surgeons of England)
FRCS (Trauma and Orthopaedics)
Diploma in Sport and Exercise Medicine
(Faculty of Sport and Exercise Medicine UK)
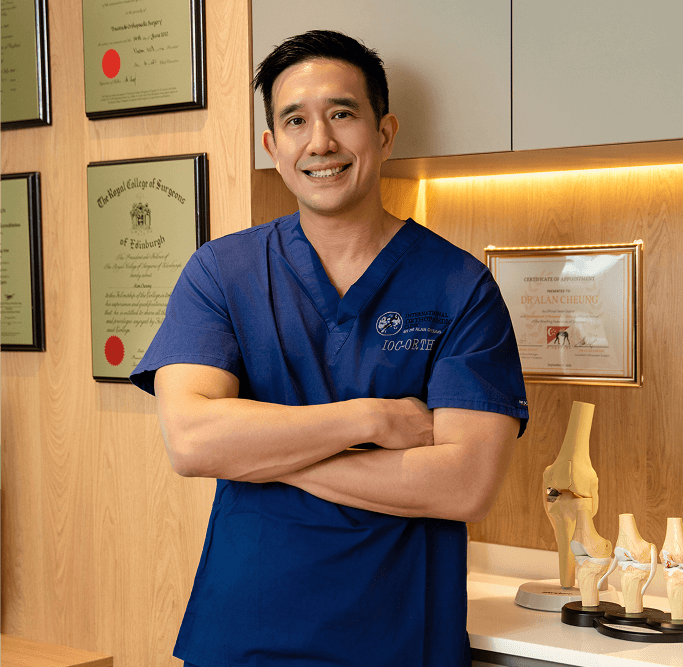
Dr Alan Cheung is an experienced knee surgeon in Singapore dedicated to helping patients with knee injuries and conditions attain optimal recoveries as quickly as possible. From non-surgical treatments to minimally invasive procedures and complex knee surgeries (including the use of robotic techniques), patients can rest assured that they will receive personalised and effective care in their best interests.
- Fellowship in Joint Reconstruction & Musculoskeletal Oncology
- Fellowship of the European Board of Orthopaedics & Traumatology
- Asia Pacific Knee Arthroscopy and Sports Medicine Society
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS)