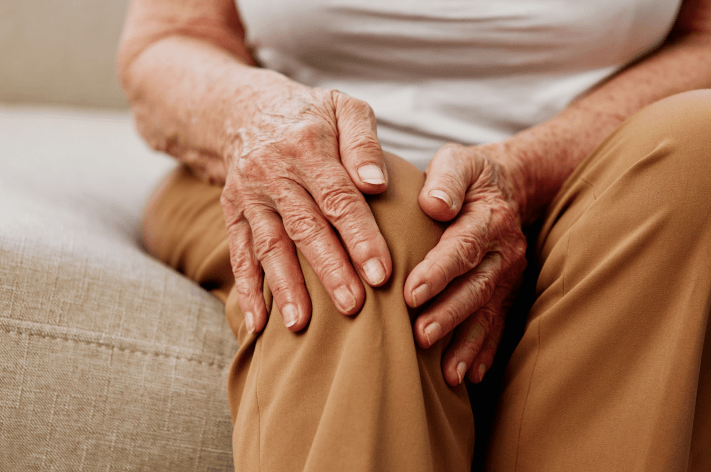
What Is Knee Arthritis?
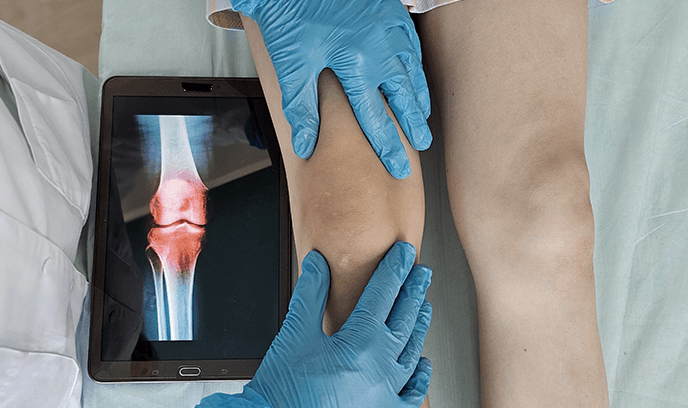
Knee arthritis is a degenerative joint condition that results in inflammation, pain, and stiffness in the knee. It occurs when the cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones wears away, leading to friction, swelling, and difficulty moving the joint.
Signs And Symptoms Of Knee Arthritis
Knee arthritis symptoms can develop gradually and worsen over time. Common signs include:
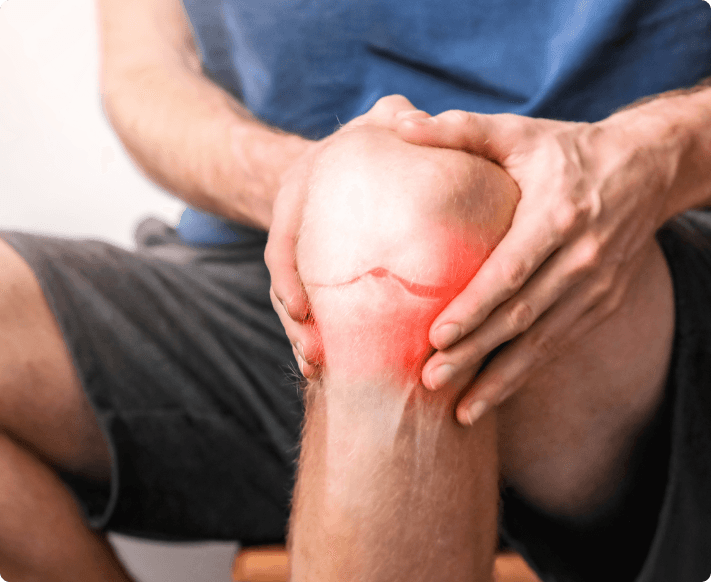
Knee Pain
: Persistent or intermittent pain, especially after activity or prolonged standing.Stiffness
: Difficulty bending or straightening the knee, particularly in the morning or after sitting for long periods.Swelling and Inflammation
: The knee may appear swollen due to fluid buildup and inflammation.Reduced Range of Motion
: Limited ability to move the knee freely.Clicking or Grinding Sensation
: A sensation of bones rubbing together due to cartilage loss.Weakness and Instability
: The knee may feel weak or give way while walking.Increased Pain with Weather Changes
: Many arthritis sufferers notice worsening pain in cold or damp weather.
If these symptoms persist or worsen, please seek medical evaluation to prevent further joint damage.