What is a Hip Labral Tear?
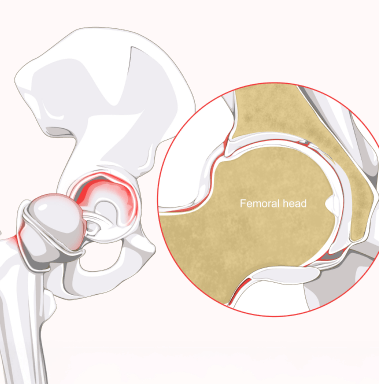
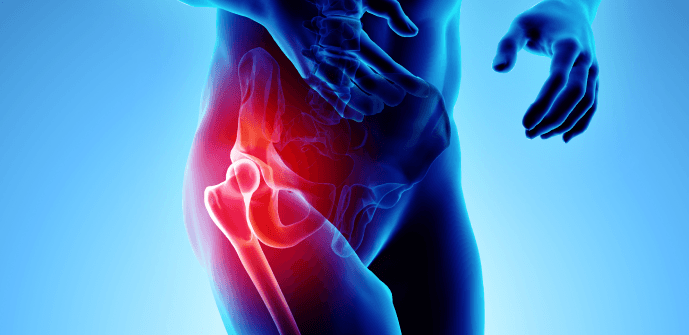
A hip labral tear is an injury to the labrum, the cartilage that surrounds the socket of the hip joint (acetabulum). The labrum plays a crucial role in stabilizing the hip joint, providing a tight seal that helps the femoral head move smoothly within the socket. When the labrum is torn, it can cause pain, instability, and a decreased range of motion in the hip joint.
Hip labral tears can occur due to trauma, structural abnormalities, or repetitive motion that places excessive strain on the hip joint. These tears are common among athletes, dancers, and individuals with hip impingement or degenerative conditions.