What is Hip Bursitis?
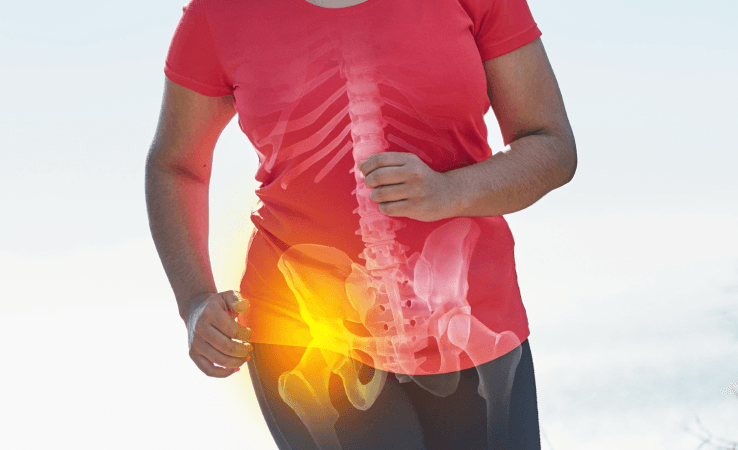
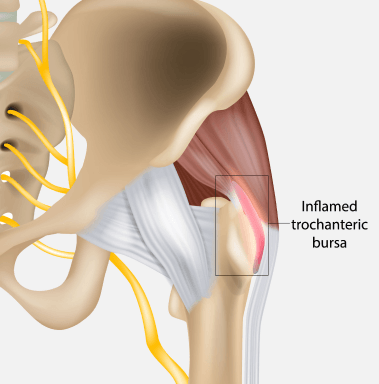
Hip bursitis is a condition that involves inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs located near the hip joint. Bursae are designed to reduce friction and cushion pressure points between the bones and tendons or muscles around the joint.
In the hip, there are two primary bursae: the trochanteric bursa and the iliopsoas bursa. The trochanteric bursa, located on the outer side of the hip, is the most commonly affected by bursitis.
When these bursae become inflamed, it results in pain and swelling, which is characteristic of hip bursitis. While hip bursitis can occur due to injury or overuse, it can also develop due to underlying conditions like arthritis.