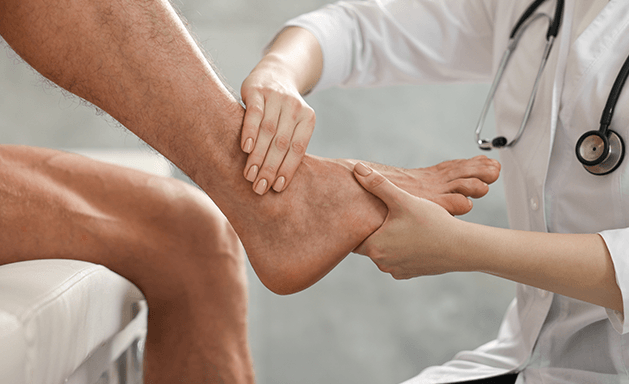
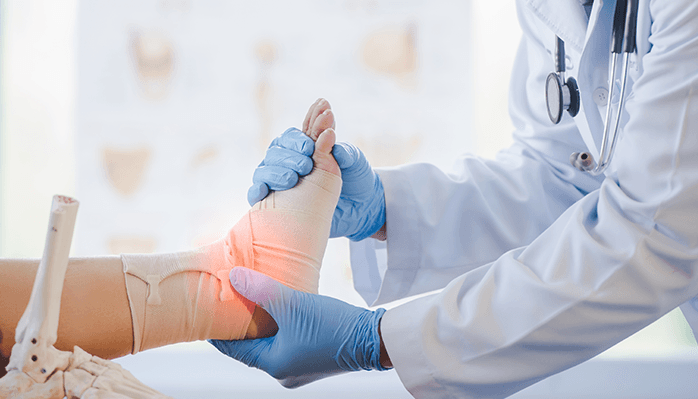
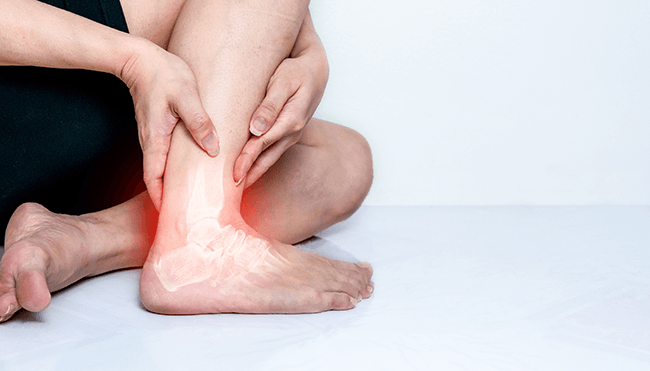
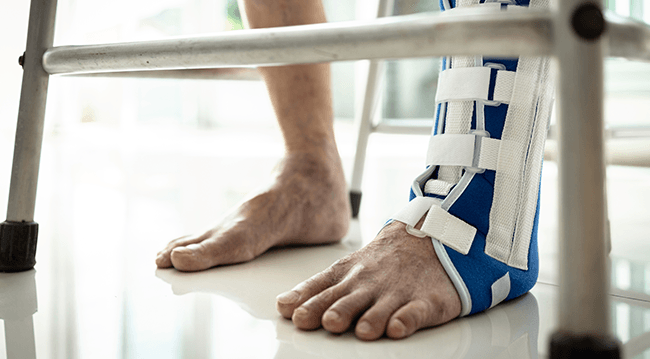
What is an Ankle Fracture?
An ankle fracture refers to a break in one or more bones that make up the ankle joint. The ankle consists of three main bones: the tibia (shinbone), fibula (the smaller bone in the lower leg), and talus (a bone in the foot that connects to the tibia and fibula).
A fracture can range from a small crack in the bone to a complete break that may involve displacement of the bone fragments. Ankle fractures vary in severity and can occur in different locations, requiring different approaches to treatment.