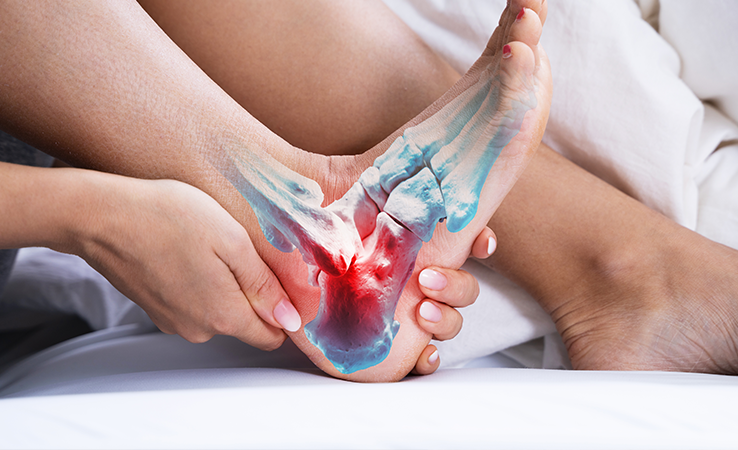
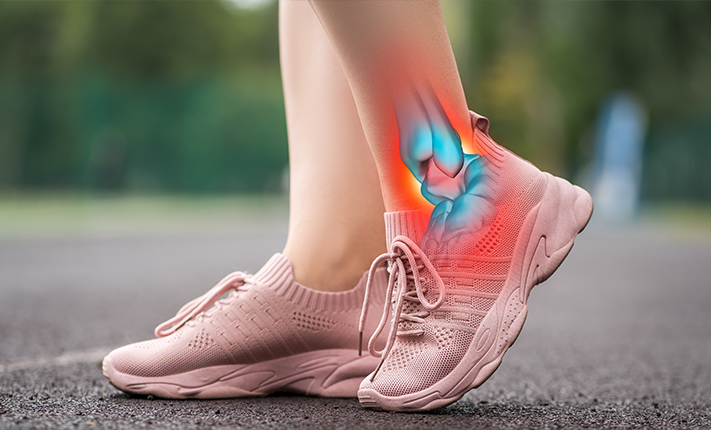
What Is Achilles Tendonitis?
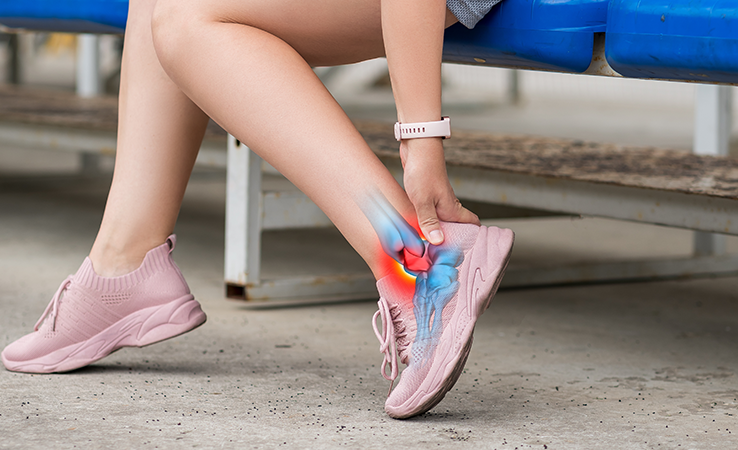
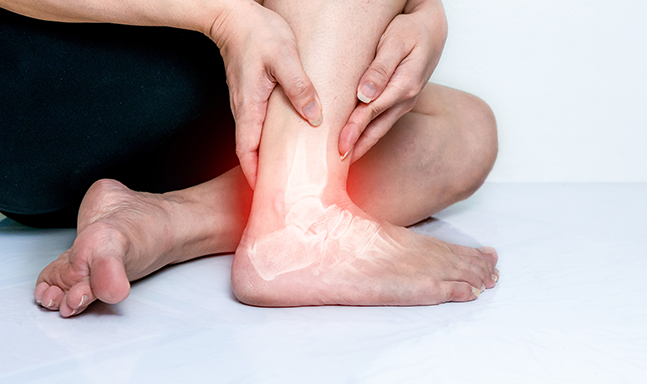
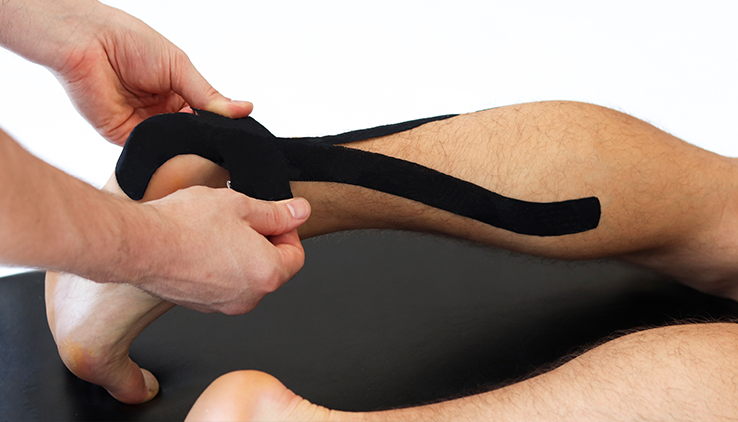
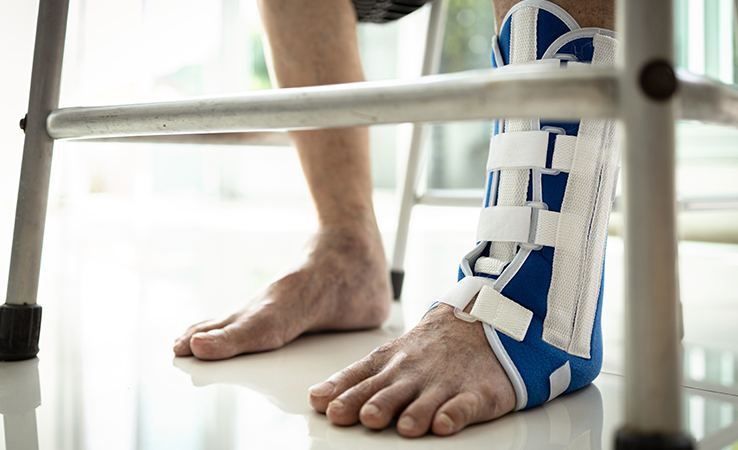
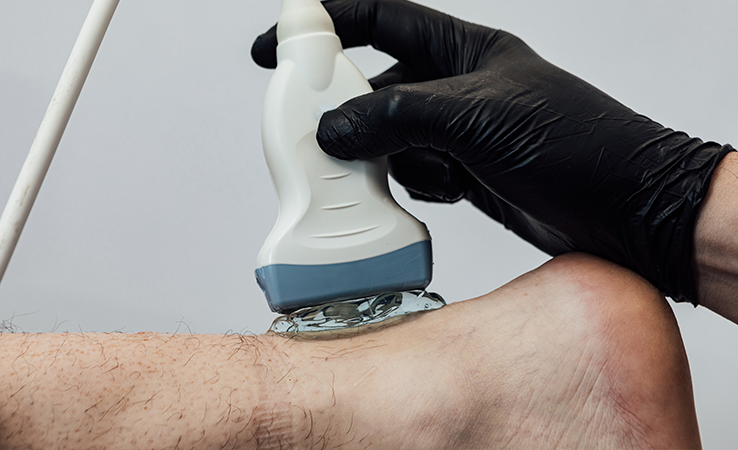
Achilles tendonitis is a condition characterised by inflammation, irritation, or degeneration of the Achilles tendon, the thick band of tissue that connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. This condition commonly affects athletes, runners, and individuals who engage in activities that involve repetitive stress on the tendon. It can cause pain and stiffness in the lower leg, particularly near the heel, and can worsen if not properly managed.